Open Shortest Path First OSPF
In order to create neighbor connections and synchronize their Link-State Databases (LSDB), Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routers oscillate between a number of distinct protocol states. In order to use Dijkstra’s method to determine the shortest path, these states guarantee that every router in a region has the same view of the network topology.
You can also read How Data Flows Through The OSI Model And It’s Importance
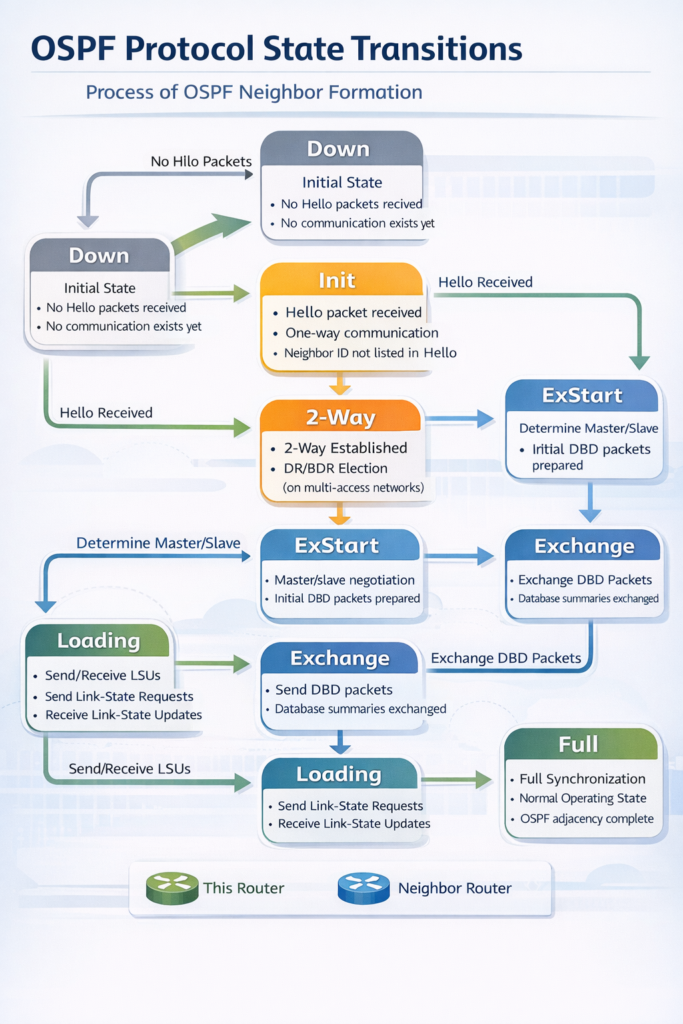
The detailed OSPF protocol states are as follows:
Down State
This is the starting point for all adjacencies under OSPF. At this point, no Hello packets have been sent to the router from the interface. The OSPF process has not yet started interacting with neighbors, which is not the same as the physical interface being down.
You can also read What Are Network Interface Cards? And Different Types Of NIC
Attempt State
Frame Relay and other Non-Broadcast Multi-Access (NBMA) networks are the only ones in this state. It means that a neighbor who is statically configured is receiving unicast Hello packets from the router, but the “dead interval” has passed and no response has been received.
Init State
When a neighbor sends a Hello packet to a router and the neighbor’s Hello packet does not yet contain the router’s own Router ID (RID), the router enters the Init state. The establishment of one-way communication is indicated by this.
You can also read Network Print Server, How It Works & Types Of Print Servers
2-Way State
In this state, both routers see their own RID in the other’s Hello packet, confirming bidirectional connectivity. The election of the Designated Router (DR) and Backup Designated Router (BDR) takes place here in broadcast or multi-access networks.
- DROthers (routers that are neither the DR nor BDR) typically stay in this stable state with one another.
- Full adjacencies are only formed with the DR and BDR.
ExStart (Exchange Start) State
In this state, routers set up a Master/Slave relationship in preparation for synchronizing their LSDBs.
- The router designated as the Master is the one with the highest Router ID.
- For the database exchange to be orderly, the Master regulates the initial sequence numbers.
- Routers often become “stuck” in this condition due to an MTU mismatch on connecting interfaces.
You can also read What is a Network Server, How it Works, Types and Components
Exchange State
Routers send and receive Database Description (DBD) packets, which are headers or brief summaries of their LSDB contents. Routers use these headers to compare their own databases and determine which Link-State Advertisements (LSAs) are out-of-date or missing. Routers create a list of Link-State Requests (LSRs) during this stage.
Loading State
To obtain the complete details of certain entries, routers issue Link-State Request (LSR) packets based on the data collected during the Exchange state. A Link-State Acknowledgment (LSAck) is sent by the receiving router in response to the neighbor’s Link-State Update (LSU) packets that contain the requested LSAs.
You can also read Why Is IP Address Important & Different Types Of IP Address
Full State
Their LSDBs are now fully synchronized, and the routers are totally nearby. Adjacent routers typically operate in this state. Before the routers can start calculating the shortest pathways and make routing decisions, they must first achieve the Full state.
Adjacency Requirements
Several parameters in the Hello packets must match precisely for routers to move from these statuses to Full, including:
- Area ID and Area Type (e.g., Stub or NSSA).
- Hello and Dead intervals.
- Subnet mask (on broadcast segments).
- Authentication passwords (if configured).
- MTU settings (required to move past the ExStart state).
You can also read What A Network Is And What Are Benefits Of Networking
