LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol
Devices on the same local network segment, including routers, switches, and wireless LAN access points, can share information about themselves with one another with LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol, a neighbor discovery protocol.
IEEE standard 802.1AB established the definition of LLDP. Before a standard protocol offering comparable functionality was established, Cisco developed its own CDP. LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol was created to offer a vendor-neutral, standardized substitute that shared CDP’s general characteristics.
How LLDP Works
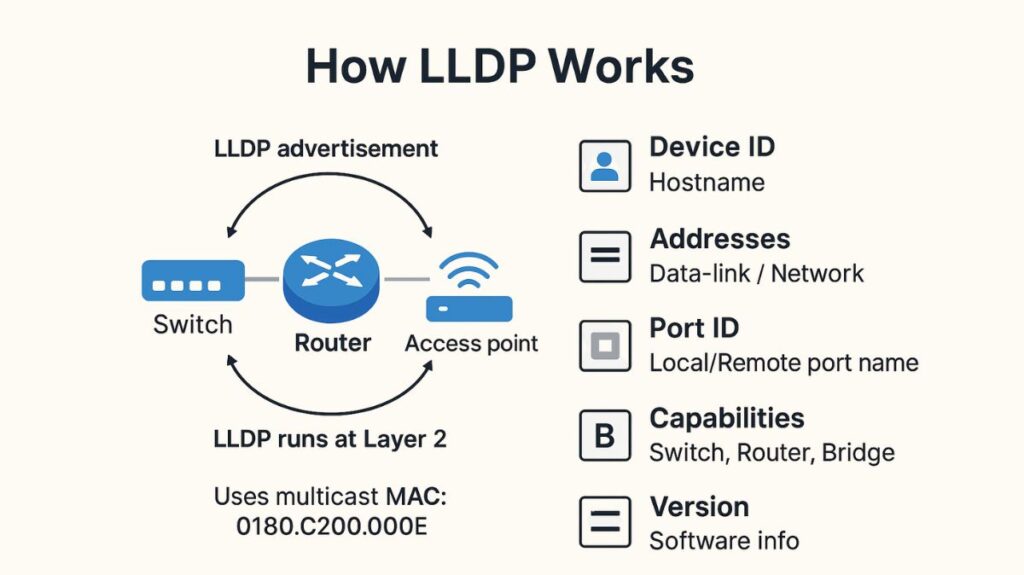
LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol uses Ethernet frames to directly encapsulate its messages and functions at the data link layer (Layer 2). LLDP may therefore find nearby devices without depending on a functional Layer 3 (IP) protocol (IPv4 or IPv6). To ensure that it only finds neighbors that are directly linked, devices do not forward LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol messages. For its communications, LLDP use a particular multicast MAC address (0180.C200.000E).
Periodically, devices that are set up using LLDP send out advertising that include personal data. Then, other gadgets that are listening to these ads find out about their neighbors.
LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol uses the following data to advertise and discover nearby devices:
Device ID: The hostname of the nearby device is usually used.
Addresses: The device’s data-link and network addresses.
Port ID: The local port’s or remote port’s name.
Capabilities: if the gadget is a switch, router, or has additional functions. Notably, LLDP varies from CDP in that it lists only the enabled capabilities rather than all supported ones and uses ‘B’ for switching (pointing to a bridge).
Version: The output can be used to determine the IOS name and version, even though LLDP does not specifically state the platform type like CDP does.
You can also read What Is A QoS Quality of Service CISCO Benefits And Types
Why LLDP is Important (Advantages)
The following are some essential functions of LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol in network administration and operations:
Vendor Interoperability: As an open standard (IEEE 802.1AB), LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol is compatible with equipment from many vendors, making it easier to find networks in mixed-vendor situations than Cisco’s proprietary CDP.
Network Discovery and Documentation: When network documentation is lacking or insufficient, it aids network engineers in learning about devices and figuring out the network topology.
Troubleshooting: Troubleshooting connectivity and configuration problems can be greatly aided by the knowledge gained through LLDP.
Layer 2 Operation: One major benefit is that it can find neighbors without depending on Layer 3 protocols (IPv4 or IPv6) being operational, which is especially useful when setting up a network for the first time or resolving IP connectivity problems.
Supports Network Management: Management platforms like Cisco DNA Center use LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol for dynamic network discovery and lifecycle management, including Day 0 installation support to automatically make new devices’ IP reachable.
Types of LLDP
There are no distinct “types” of LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol in the same sense that a network may have various kinds of traffic. Sending out messages known as LLDPDUs, which are made up of several Type-Length-Value (TLV) structures, is how LLDP works. These TLVs, which fall into three categories mandatory, voluntary, and organizationally specific define the various forms of LLDP.
Required TLVs
These must be present in every LLDPDU since they are the fundamental components of any LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol message. They give a device the very minimum of information needed to recognize itself and its connecting point.
- The device or system is uniquely identified by its Chassis ID TLV (Type 1), which might be its MAC address or a user-defined name.
- The device from which the LLDPDU is being delivered is uniquely identified by the Port ID TLV (Type 2).
- Time To Live TLV (Type 3): Indicates how long the advertised data should be stored on the receiving device before it expires.
- End of LLDPDU TLV (Type 0): The LLDPDU frame ends with this unique TLV.
Optional TLVs
These TLVs offer more thorough details regarding the gadget and its features. Which of these to include in their LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol ads is up to the network administrators.
- A textual description of the port is provided by the Port Description TLV (Type 4).
- System Name TLV (Type 5): The hostname of the apparatus.
- Description of the System TLV (Type 6): A thorough explanation of the hardware, operating system, and software version of the device.
- The device’s main functions (such as bridge, router, and WLAN access point) are indicated by the System Capabilities TLV (Type 7).
- Management Address TLV (Type 8): The IP address and additional data required for remote device management.
Organizationally Specific TLVs
Custom, vendor-specific TLVs can be defined using LLDP. These are employed to support specialized functions or to add proprietary information to LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol. LLDP-MED is the most widely used example.
The TIA (Telecommunications Industry Association) created LLDP for “plug and play” functionality of VoIP phones and other media endpoints. LLDP-MED (Media Endpoint Discovery) is a significant extension of LLDP. For certain devices, LLDP-MED TLVs offer vital information like:
- Network Policy TLV: Offers Layer 2 and Layer 3 QoS configurations for voice traffic, such as VLAN ID and DiffServ code points.
- Position Identification TLV: Notifies emergency services of the device’s precise position.
- A device can negotiate a certain quantity of power from the switch using Power over Ethernet (PoE) TLV.
- Because of its modular, TLV-based design, LLDP is a versatile and expandable network discovery protocol.
You can also read Cisco Discovery Protocol, How CDP Works, And Benefits of CDP
Disadvantages of LLDP
Not Enabled by Default on Cisco Devices: On Cisco equipment, LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol must be globally enabled because it is normally disabled by default, in contrast to CDP.
LLDP-MED Incompatibility: It is not possible to use LLDP-MED and standard LLDP together.
Resource Usage: Even though active protocols typically have modest overhead, they do use some network bandwidth and CPU power.
Applications of LLDP
In a variety of network settings, LLDP is utilized to facilitate management, documentation, and discovery:
Network Topology Mapping: LLDP data can be used by automated systems to generate and show network topology maps.
Day 0 Device Installation: Applications can use LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol for “Plug and Play” operations to find new devices and connect them to the internet without requiring human IP setting.
Troubleshooting: Verifying connections and device types can be aided by LLDP in cases where documentation is lacking or insufficient.
Voice VLANs: While Cisco IP Phones may also use CDP to learn VLAN IDs, LLDP-MED is specifically made to operate with audio applications.
Converged Wired and Wireless Management: With the help of LLDP and CDP, integrated management platforms may control wired and wireless LANs from a single interface.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) negotiation: Although not specifically mentioned in the LLDP-MED sources that are supplied, the reference to “power level” in connection with LLDP-MED capabilities suggests that it is used in PoE negotiation for devices such as IP phones.
Configuration and Verification
There are some significant distinctions between CDP and LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol configuration and verification on Cisco devices.
Global Configuration
To turn on LLDP globally on a device (which turns it on by default on all interfaces):
lldp runTo disable it globally:- no lldp run
Interface-Specific Configuration
LLDP allows separate control for sending (transmit) and receiving (receive) messages on an interface:
- To enable transmission:
lldp transmit - To disable transmission:
no lldp transmit - To enable reception:
lldp receive - To disable reception:
no lldp receive
Timer and Holdtime Configuration
- Periodically, advertising for LLDP are sent. There are two possible default intervals: 30 and 60 seconds.
- Additionally, the advertised LLDP hold time is adjustable. There are two default hold times: 120 and 180 seconds.
- Reinitialization delay is the amount of time (e.g., 2 seconds) that the device waits after LLDP is disabled on a port before accepting a configuration to re-enable it.
Verification Commands
LLDP verification commands are comparable to CDP commands, typically substituting lldp for the keyword cdp.
show lldp: Displays global LLDP information, including status, advertisement interval, hold time, and reinitialisation delay.show lldp interface [type number]: Shows whether LLDP is enabled for transmitting and receiving on each interface or a specific interface.show lldp neighbors [type number]: Lists a summary line of information about each neighbor.show lldp neighbors detail: Provides a detailed set of information (approximately 15 lines) for every neighbor.show lldp entry hostname: Displays the same detailed information asshow lldp neighbors detailbut only for the named neighbor.show lldp traffic: Displays global statistics for the number of LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol advertisements sent and received.
You can also read What Is Routing Loop Prevention? Guide To Network Stability
