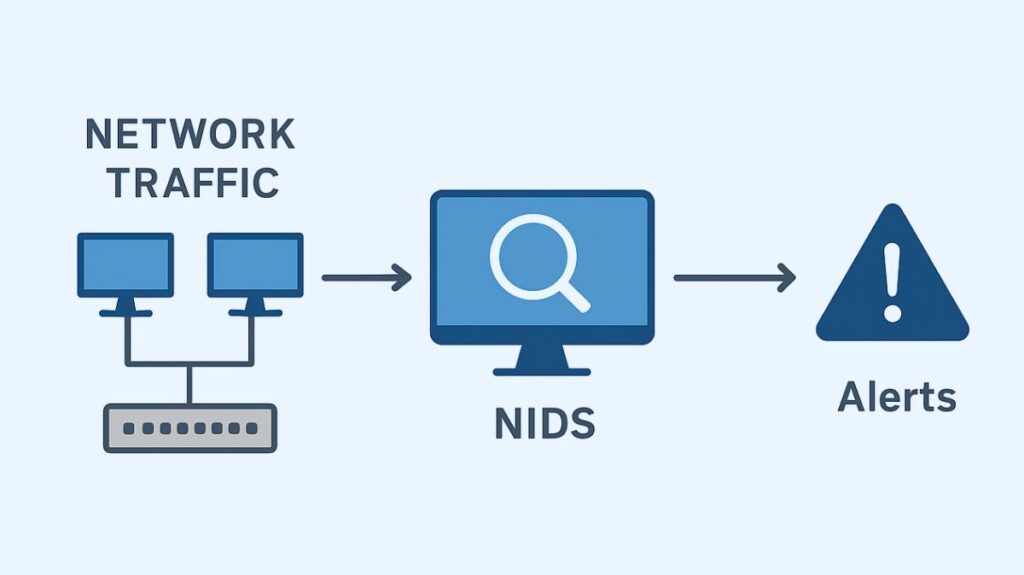
Network Based Intrusion Detection System NIDS
Using techniques like signature-based detection, which compares traffic to known attack patterns, or anomaly-based detection, which identifies deviations from typical network behavior, a network intrusion detection system (NIDS) keeps an eye on a network’s traffic for suspicious or malicious activity and sends out alerts when threats are discovered. In order to detect and address security threats like DoS attacks, illegal access attempts, and malware infections before they cause harm, NIDS are an essential component of a larger security architecture.
Also Read About What is SSH in Networking, Architecture and Uses of SSH
Core Function and Nature
Monitoring and reporting are the main responsibilities of an NIDS.
Detection, not Prevention: An IDS is a passive detection system; it is not a prevention system. Although it can identify the existence of an attack, it cannot stop illegal access. In a network, it serves as a type of audit control.
Reporting and Alerting: The IDS records information and issues an alert when an attack is discovered. Every apparent threat is rated, and the threats are reported.
Real-Time Monitoring: Intrusion detection entails keeping an eye on network activity in real-time and analyzing data to look for possible weaknesses and ongoing attacks. By removing the hacker from the network, this real-time feature can drastically lower possible harm and recovery expenses.
Alerting: The NIDS sends out alerts to administrators so they may look into and address any questionable activities. It rates each perceived threat and logs the data. Protocols like SNMP, Security Device Event Exchange (SDEE), and Syslog can be used to provide alerts.
An effective intrusion system is defined by its ability to operate continuously without human oversight and its fault tolerance, which allows it to withstand system crashes without requiring the rebuilding of its knowledge base upon restart.
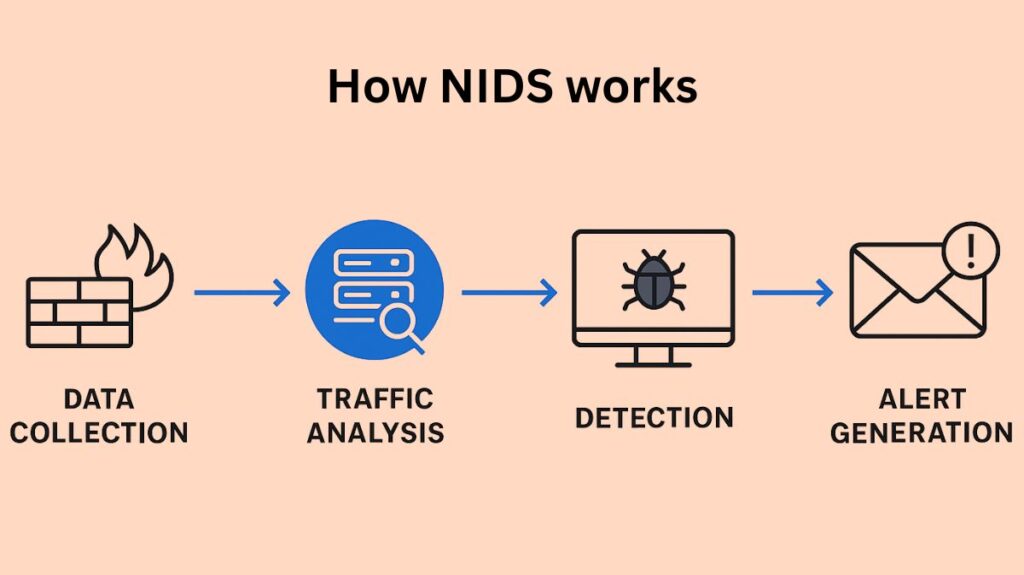
How NIDS Works?
In order to monitor traffic going to and from every device on a network segment, an NIDS is usually placed at key locations inside the network, such as behind a firewall.
Data Collection: Real-time network traffic (data packets) is recorded by the NIDS sensors. They frequently work in a passive manner, copying and examining packets without immediately affecting the flow of traffic.
Traffic Analysis: The system examines the intercepted packets using complex algorithms. Examining packet payloads (for malicious content) and headers (for questionable IPs or ports) may be part of this analysis.
Detection: Using one or more detection techniques, the NIDS compares the examined traffic to its threat intelligence.
Alert Generation: Security staff receive an alert from the NIDS if it detects unusual activity or a possible threat. In order to facilitate investigation and response, this warning often contains information about the suspected conduct.
Also Read About Types Of Routing Protocols, It’s Core Functions And Purpose
Primary Detection Methods
IDS sensors use a variety of techniques to detect malicious traffic, including:
- Signature-Based Detection: This technique uses a database of signatures, which are collections of rules that search for particular traits or patterns in individual packets or packet streams. The most important technique in use now is this one. To stay up to date, signatures need to be changed on a regular basis.
- Anomaly-Based Detection: This technique creates a baseline of typical network activity (such as the typical amount of TCP sender requests that go unanswered) and takes action when it detects notable departures from that baseline. This feature, which is frequently called anomaly detection, is employed to detect propagating worms and other similar threats.
- Policy-Based Detection: This method can assist in preventing unknown attacks that do not fall within the permitted policy by comparing traffic to manually written policy rules to decide whether the traffic should be allowed or prohibited.
- Reputation-Based Filtering: This filters traffic using reputation ratings after gathering data from systems all over the world (global correlation) to detect known bad actors based on IP addresses, URLs, DNS domains, etc.
Alerts generated by the sensor can be sent in real time to a monitoring system via protocols including Security Device Event Exchange (SDEE), Syslog, and SNMP.
Important Characteristics, Identified Risks, and Restrictions
An NIDS offers improved network visibility and continually analyzes all network traffic.
Important characteristics include:
- Network monitoring in real time.
- Threat identification and notification.
- Analyze and report logs.
- Connection to additional security technologies, such Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems or firewalls.
Numerous hazards and problems can be identified by NIDS, including:
- Attacks known as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) and Denial of Service (DoS).
- Suspicious connections and port searches.
- Malware.
- Efforts at unauthorized entry.
- Infractions of the policy, like illicit connections or unapproved apps.
Also Read About Difference Between DoS Vs DDoS Attack, Types & Advantages
Limitations
Notwithstanding its benefits, NIDS has many drawbacks:
- It is unable to stop attacks.
- False positives, or marking harmless traffic as malicious, could result from it.
- To evaluate and react to the generated alerts, qualified staff is needed.
- The original packet might be on its way to its destination before the alert is created because it examines a replica of the packet.
Security Onion, Suricata, Bro/Zeek, and Snort (by Cisco) are typical examples of NIDS tools.
