In this article, we learn about Internet Control Message Protocol, how it works, History and Evolution, why ICMP is Important, Types of ICMP Messages, applications, disadvantages and Security Risks.
What is ICMP and How it Works
ICMP is a communications service provider and IP management protocol. As a component of Layer 3 (the network layer), ICMP is independent of TCP or UDP, in contrast to application protocols that employ these transport protocols. IP datagrams are used to encapsulate their messages. To indicate that the data being transported is part of the ICMP protocol, for example, the Protocol field in an IP header contains the value 0x01 (or 01h). This implies that all data or segments must go via IP.
Hosts receive information about network issues from ICMP messages. It’s crucial to remember that ICMP merely notifies the sender of these issues; it doesn’t fix them. Additionally, in order to stop congestion from cascading error reports, errors produced by ICMP messages do not themselves generate additional ICMP messages.
You can also read Advantages And Disadvantages Of SNMP, How SNMP Work
History and Evolution
The TCP/IP protocol suite has included ICMP for a very long period. The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) created the TCP/IP paradigm, which includes ICMP, to guarantee data integrity and preserve communications even in the case of a catastrophic incident.
As Internet Protocol Version 4 gave way to IPv6, ICMP changed as well. ICMPv6 is the name of ICMP for IPv6. ICMPv6 is an integral component of IPv6 and is transmitted as an extension header following the main IPv6 header, in contrast to ICMPv4, which is a distinct Layer 3 protocol. A value of 58 in the IPv6 packet’s Next Header field designates ICMPv6.
Why ICMP is Important (Advantages)
ICMP plays a crucial role in network operations for several reasons:
- Diagnostics and Troubleshooting: It is the primary tool for testing basic IP connectivity without relying on higher-layer applications. Tools like
pingandtracerouteextensively use ICMP messages.
- Network Management: Devices utilize the messages defined by ICMP to assist in managing and controlling the IP network. Along with other information pertinent to IP packet processing, it reports faults.
- Reliability for IP: ICMP assists in detecting delivery process faults, even if IP is connectionless and unreliable in and of itself.
- Basic Connectivity Testing: Layers 1, 2, and 3 of the OSI model are tested using the ping command, which uses ICMP echo requests and answers to verify that the network can send a packet from one host to another and back.
Types of ICMP Messages
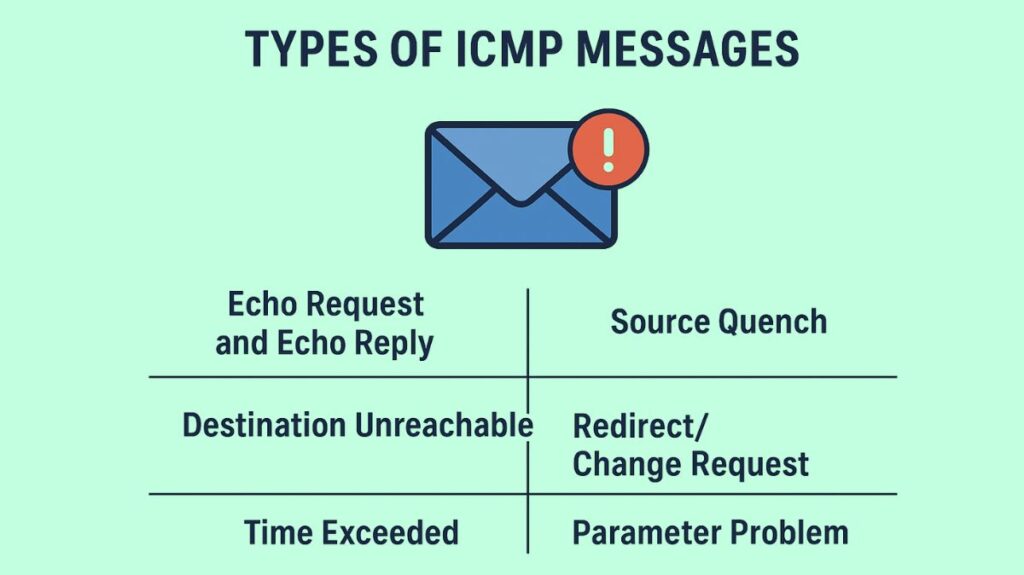
ICMP defines various messages for error reporting and control functions.
Common ICMPv4 Messages:
Echo Request and Echo Reply: The ping command uses echo request and echo reply to check device connectivity. An echo reply is anticipated in response to an echo request.
Destination Unreachable: Because a router is unable to send an IP datagram further, for instance, because there is no known path to the destination, it sends the message “Destination Unreachable.” Unreachability might be caused by host, protocol, port, network, or fragmentation requirements.
Time Exceeded: If an IP datagram crosses its hop limit (Time To Live, or TTL) before reaching its destination, it is sent with the message “Time Exceeded.”
Source Quench/Buffer Full: Indicates congestion when a router’s memory buffer for incoming datagrams is full.
Redirect/Change Request: When a gateway indicates that a better gateway is available for a distant network, it initiates a redirect/change request, which tells a host to utilize a particular router for a given destination.
Parameter Problem: An issue in an IP header field is indicated by the parameter problem.
Timestamp Request/Reply: Assists in calculating the overall network transit time as well as the time on a remote host. Keep in mind that clock synchronization is more consistently performed via Network Time Protocol (NTP) at higher tiers.
Information Request/Reply: Originally designed to help hosts figure out their network number, this protocol is currently regarded as outdated and has been superseded by BOOTP and DHCP.
Address Mask Request/Reply: Used to find a network’s subnet mask.
Common ICMPv6 Messages and Features: ICMPv6, as described in RFC 2463, has extra IPv6 messages in addition to supporting ICMPv4 messages.
Destination Unreachable (Type 1): A packet that is marked as “Destination Unreachable” (Type 1) cannot be forwarded.
Packet Too Big (Type 2): Notifies the source node of the maximum transmission unit (MTU) permitted by a restrictive link, preventing fragmentation in IPv6.
Time Exceeded (Type 3): Signals that a packet’s hop limit has been reached, same like IPv4.
Echo Request (Type 128) and Echo Reply (Type 129): Like ping in IPv4, these are used to evaluate connectivity.
Router Solicitation (RS, Type 133): Hosts use router solicitations (RS, Type 133) to ask nearby routers for instant router advertisements so they can get prefix information.
Router Advertisement (RA, Type 134): In response to RS or on a regular basis, routers transmit these messages (multicast to all-nodes address FF02::1) with prefix information.
Neighbor Solicitation (NS, Type 135) and Neighbor Advertisement (NA, Type 136): Part of the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP), which takes the place of ARP in IPv4, Neighbor Solicitation (NS, Type 135) and Neighbor Advertisement (NA, Type 136) are used to resolve the MAC addresses of IPv6 neighbors and preserve reachability data.
Path MTU Discovery (PMTUD): An ICMPv6 procedure that stops fragmentation is called Path MTU Discovery (PMTUD).
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD): In IPv6, Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) takes the place of IGMP in order to allow hosts to join multicast groups.
Duplicate Address Detection (DAD): In IPv6, duplicate address detection, or DAD, is used to guarantee address uniqueness.
You can also read Network Device Maintenance Applications And How It Works
Applications
The primary applications of ICMP are network diagnostic and troubleshooting tools:
Ping (Packet Internet Groper): Tests a device’s reachability and fundamental connectivity on an IP network using ICMP echo request and echo reply messages. Evaluating layers 1, 2, and 3 of the OSI model verifies whether the network can send a packet from one host to another and back.
Traceroute (or tracert on Windows): Traceroute, often known as tracert on Windows, uses ICMP time-outs to indicate each router that a packet passes through on its way across an internetwork.
Disadvantages and Security Risks
While essential, ICMP also presents potential security vulnerabilities:
Network Mapping: Attackers can learn about the topology of the network and the devices that are currently connected by using ICMP messages, such as host unreachable messages or echo requests.
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Attacks known as denial of service (DoS) can be launched using specific ICMP messages. Smurf attacks, for example, use ICMP. Without affecting operations, ICMP redirection can be disabled to remove a potential attack vector. Attackers can also be prevented from obtaining network mapping information by turning off ICMP unreachable.
Packet Amplification Attacks: ICMPv6 has been linked to packet amplification attacks in IPv6.
Filtering Challenges: Although ICMP packets can be filtered by type and code using Access Control Lists (ACLs), improperly designed inbound ACLs may unintentionally ignore valid overhead protocols, such as routing protocol messages.
More Details
- One of the fundamental protocols in the TCP/IP architectural model’s Internet layer is ICMP.
- Through Requests For Comments (RFCs), the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) upholds TCP/IP standards, including ICMP standards.
- The “Protocol” field in the IP header designates the network layer or upper-layer protocol, such as ICMP and ARP. The protocol number allocated to ICMP is 1.
- An ICMP destination unreachable message is returned to the sender by a router when it is unable to deliver a packet.
- The alphabet is usually used by the ping command as a payload in the data section of the ICMP packet; by default, this payload is around 100 bytes.
- Redirecting hosts to the optimal router, neighbor solicitation and advertisement (which locates MAC addresses for IPv6 neighbors), and router solicitation and advertisement are further uses for ICMPv6. IPv4 ARP and ICMP Router Discovery are replaced by the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP), a component of ICMPv6.
You can also read CISCO IFS IOS File System Advantages And Disadvantages
