In this article, we learn about Security Assertion Markup Language, Components of SAML, How SAML Works, How SAML Authentication Works and Benefits of SAML
Security Assertion Markup Language
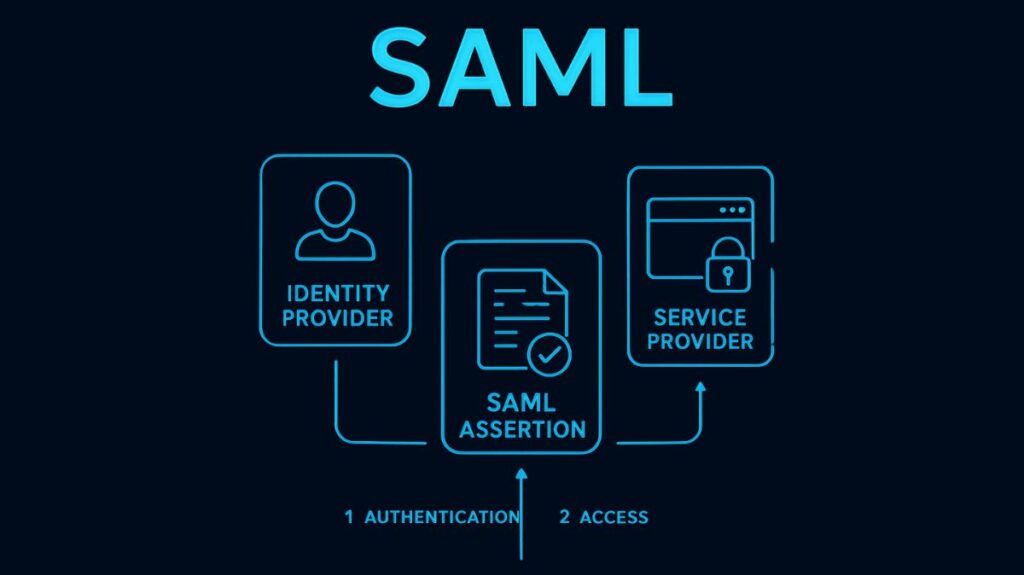
An XML-based framework is used by the open Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) to safely transfer authorization and authentication information between various systems or security domains.
SAML is a standardized method of verifying that a user is who they say they are. Its main goal is to enable Single Sign-On (SSO) for web applications, which enables a user to authenticate only once and access several services or apps without having to enter their login information again. SAML is frequently used for cloud-based business software authentication and is extensively supported in organizations.
You can also read What is Open System Authentication OSA and How it Works?
Components of SAML
SAML transactions involve three main roles:
- Principal (The User/Subject): The person trying to access a protected resource, usually using a web browser.
- Identity Provider (IdP): The system that maintains a user’s identification, authenticates them (for example, through MFA, LDAP, or a password), and verifies their identity to the service provider is known as the Identity Provider (IdP). Okta and Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD) are two examples of IdPs.
- Service Provider (SP): The resource or application that the user wishes to access is known as the service provider (SP). Instead of handling its own login procedure, the SP uses the given assertion to authorize access and depends on the IdP to confirm the user’s identity. Salesforce and AWS are two instances of SPs.
Because they exchange identity authentication and authorization information, the IdP and the SP are both regarded as SAML providers.
How SAML Works
The SAML Assertion, the core mechanism of SAML, functions similarly to a digitally signed passport or a security information packet. The IdP creates, issues, and transfers this XML document to the SP. To make sure the data is genuine and hasn’t been altered in transit, the SP verifies the digital signature on the claim.
The service provider uses the specific statements in SAML assertions to decide how to implement access control. There are three primary categories of assertions:
- Authentication Statements: Verify the user’s identity using authentication statements, which include the time and method of authentication (e.g., password, multi-factor authentication).
- Attribute Statements: Give the SP precise information about the user, like their email address, department, or job, so they may utilize it for authorization.
- Authorization Decision Statements: Declare in Authorization Decision Statements if the user has been expressly authorized or denied access to a requested service by the IdP.
You can also read What is Kerberos, Limitations of Kerberos and Components
How SAML Authentication Works (Simplified SP-Initiated Flow)
The most common flow, known as Service Provider-Initiated SSO (or the Web Browser SSO Profile), follows these general steps:
- Access Attempt: A protected service (SP) is attempted to be accessed by the user (Principal).
- Redirect: When the SP determines that a user is not authorized, it creates a SAML Request and sends the user’s browser to the Identity Provider (IdP).
- Authentication: The IdP confirms the user’s identity and asks for login information if they haven’t previously.
- Assertion Transfer: The digitally signed SAML Assertion is generated by the IdP and returned to the user’s browser as part of a SAML Response.
- Access Granted: The SAML Response is sent to the SP’s Assertion Consumer Service by the user’s browser. Without requiring a new login, the SP establishes a security context, verifies the assertion’s signature and content, and allows the user access to the requested resource.
Benefits of SAML for Businesses
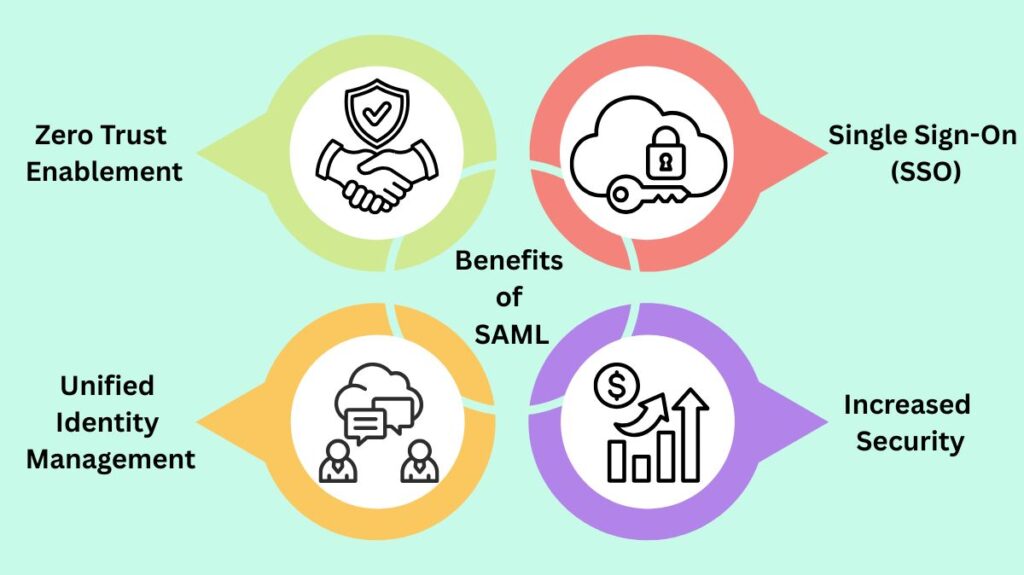
SAML has various organizational and security benefits, making it the cornerstone of enterprise single sign-on.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): It enhances user ease and experience by allowing users to access numerous applications with a single set of login credentials.
- Increased Security: Credentials are only delivered to the secure IdP and are not distributed around applications. The centralization of authentication at the IdP. This enables businesses to implement robust, centralized security measures, such as mandating conditional access or multifactor authentication (MFA) for all SAML-capable applications.
- Unified Identity Management: IT teams can handle authorization and authentication from a single system with unified identity management, which streamlines user provisioning and lowers administration overhead.
- Zero Trust Enablement: By enabling tech teams to apply regulations and validate each access request based on user behavior, device, or location, SAML supports a Zero Trust security approach.
You can also read What is Diameter protocol Explained, Applications & Commands
SAML vs. OAuth/OpenID Connect
SAML is often compared to OAuth and OpenID Connect (OIDC), but they serve slightly different primary goals:
| Feature | SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) | OAuth 2.0 / OpenID Connect (OIDC) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Authentication (Who the user is) and authorization, primarily in an Enterprise/B2B context. | Authorization (What the user is allowed to do) in a Consumer/Mobile context, with OIDC adding authentication. |
| Data Format | XML (SAML Assertion). | JSON (JWT Tokens). |
| Typical Use | Centralized SSO for corporate applications (e.g., logging into Salesforce via a company portal). | Delegated access to third-party apps (e.g., “Log in with Google”). |
While SAML facilitates the confirmation of a user’s authentication (verifying their identity), it is separate from authorization, which refers to the user’s privileges or what actions they are permitted to perform within the system.
You can also read What is EAP AKA, How it Works, Advantages and Disadvantages
