CCNA Chef

CCNA Chef is an open-source configuration management tool that automates infrastructure deployment and management by treating infrastructure as code (IaC). It was originally developed by Opscode, and is currently available in a series of commercial solutions under the moniker Progress Chef. Chef’s fundamental configuration files, called cookbooks and recipes, are written in a Domain Specific Language (DSL) based on Ruby.
Chef is designed to streamline the arduous work of configuring and managing a company’s servers, ensuring that system configurations remain consistent, predictable, and scalable across diverse environments, including on-premise, cloud, and hybrid installations.
CCNA Chef Architecture and Operation
CCNA Chef operates utilizing an agent-based design and a pull methodology.
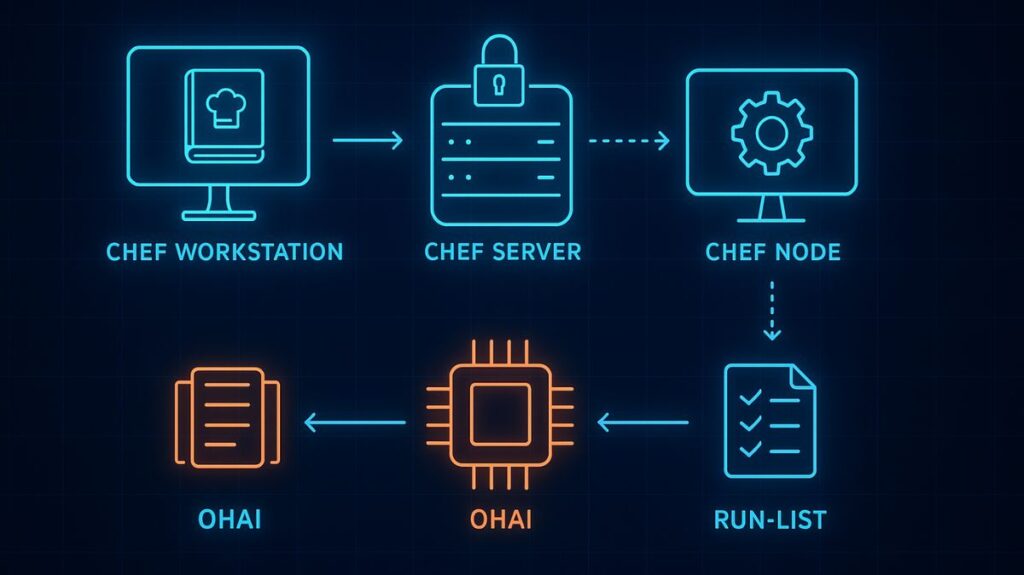
Chef Server: This operates as the central repository and single source of truth for all configuration data, policies, cookbooks, recipes, and metadata. Any modifications made to the infrastructure code must travel through the Chef Server to be deployed.
Chef Workstation: This is the machine used by administrators or DevOps engineers (“Chefs”) to author, test, and manage the configuration code. Command-line tools like Knife are used from the workstation to upload material to the Chef Server and communicate with nodes.
Chef Nodes (Clients): These are the managed computers (physical, virtual, or cloud instances). The Chef Client, which serves as the agent, needs to be installed on every node. The Chef Client frequently connects the Chef Server to get the latest configuration policies and recipes (the pull model), and then runs them to guarantee the node is in the proper condition.
CCNA Chef Key Configuration Concepts
Chef configuration is structured using specified building blocks:
Cookbooks: These are collections of recipes and accompanying files (such as templates, files, and metadata) that encapsulate the whole configuration logic required for a given system component or application, like an Apache Web Server.
Recipes: The primary unit of configuration within a cookbook. A recipe is a script written in Ruby DSL that outlines a sequence of resources that should be in a particular state on the node.
Resources: The intended state of a system component is described by these declarative definitions found in a recipe. Examples include managing packages, services, users, or files on the node.
Runlist: This is an ordered list of recipes or cookbooks that the Chef Client executes against a specific node to ensure a controlled configuration workflow.
Ohai: A utility deployed on every node that collects system details such as CPU, memory, OS version, and network configuration and communicates this metadata to the Chef Server.
You can also read What is REST API, Benefits of REST API, and Applications
Advantages of Using CCNA Chef
Continuous Deployment: Continuous software deployment allows the business to stay up to date with market demands and shifting consumer preferences for a given product. In order to survive in the cutthroat software market, we must constantly innovate and have a toolkit that facilitates quick, continuous deployment.
Increase System Robustness: Big tech giants have large server farms and need redundant servers to manage a few infrastructure automation is needed to detect and fix all issues before software deployment to prevent server outages from crippling the entire organization.
Adaption to the cloud: Chef effortlessly interfaces with infrastructure on the cloud for one shot automation. Major cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and GCP are easily integrated with it.
Managing Data Centers and Cloud Environments: It is used by huge IT businesses to manage their cloud infrastructure, under chef we can control all your cloud and on-premise platforms including servers.
You can also read What is Network Configuration Management NCM & its Benefits
Disadvantages of CCNA Chef
- One of the main downsides of Chef is the way cookbooks are managed. It needs constant babying so that those who are working should not screw up with others cookbooks.
- If someone is unfamiliar with Ruby, learning is difficult.
- Good Documentation is still needed.
CCNA Chef Features and Comparative Context
Chef is highly recognized for its versatility and stability, especially for large-scale deployments in public and private environments. It provides outstanding cloud technology integration, including Google Cloud Platform, AWS, and Azure.
However, when compared to agentless solutions like Ansible, Chef has a few major distinctions:
Language and Learning Curve: Chef employs Ruby DSL, which is aimed towards developers and can result in a longer learning curve if the user is not already familiar with Ruby.
Agent Requirement: Because of its agent-based architecture, each system being controlled (the target nodes) requires the installation and upkeep of particular software (the Chef Client and its dependencies).
Modern Chef versions, including Chef Infra 18, have been improved with native interaction with Kubernetes and built-in compliance scanning using InSpec, enabling unified configuration management across traditional and containerized infrastructure.
You can also read Ansible CCNA Architecture, Components And Key Features
