VTP vlan trunking protocol
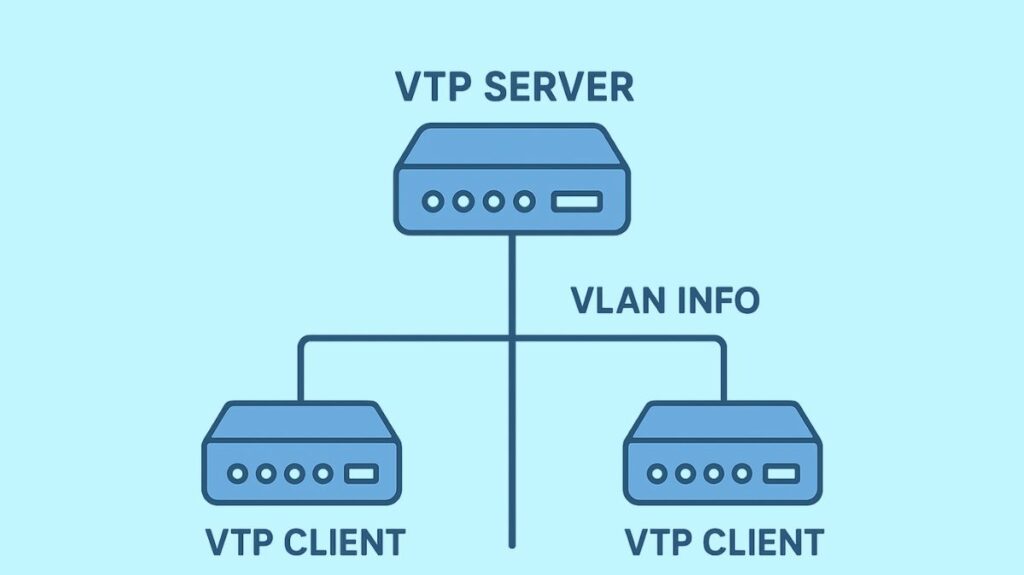
The Cisco proprietary Layer 2 messaging protocol known as VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) was created to control and synchronize VLAN configurations among a network of Cisco switches that are part of a VTP domain. Its main objective is to simplify maintenance and eliminate the need for manual configuration on each switch by automatically propagating VLAN database updates from a VTP server to VTP clients.
What does the VLAN trunk protocol vtp do?
VTP functions at Layer 2 and exchanges VTP ads via trunk lines, usually IEEE 802.1Q or Inter-Switch Link (ISL) frames. Important details about the VLAN database can be found in these ads.
Also Read About What Are Layer 2 Switches And How Does Layer 2 Switch Work
Important mechanisms consist of:
VTP Domain Name
A logical collection of switches that exchange VLAN data is called a VTP domain name. Every switch in a VTP domain needs to have the same name. Only one VTP domain may be associated with a switch at a time. A switch will use the domain name from the first VTP packet it receives if no domain name is set.
Configuration Revision Number
A 32-bit value that tracks modifications to the VLAN database and specifies the degree of revision for a VTP packet. A VTP device’s configuration revision is increased by one whenever a VLAN change is made. Other switches update their VLAN databases to reflect the most recent version of the switch, which is the one with the highest revision number. The VTP domain name can be changed and then changed again to reset a switch’s configuration revision.
VTP Advertisements (Messages)
VTP communicates VLAN information using a variety of message formats. To guarantee that all VLAN configurations within a domain are synchronized, VTP servers broadcast them on a regular basis or whenever something changes.
Summary Advertisements
Notify neighbouring switches of the current VTP domain name and configuration revision number by sending these messages by default every five minutes or whenever a VLAN configuration changes.
Subset Advertisements
When a VLAN configuration changes, heed summary ads that provide a list of VLAN details.
Advertisement Requests
When a switch requires VLAN information, such as following a reset, a change in the VTP domain name, or when it receives a summary advertisement with a higher configuration revision than its own, it sends out advertisement requests. The multicast MAC address 01-00-0C-CC-CC-CC is where VTP ads are sent.
VTP Modes of Operation
Three VTP operating modes are supported by Cisco Catalyst switches:
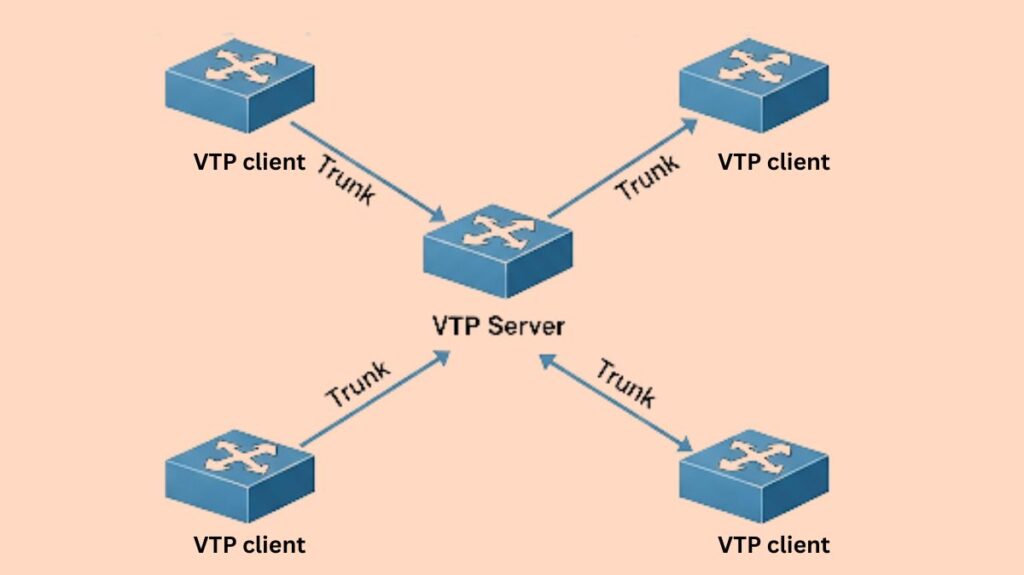
Server Mode: All Catalyst switches operate in this mode by default. A switch is permitted to add, edit, and remove VLANs in this mode. Any modifications made to a server are stored in NVRAM and broadcast to the whole VTP domain. At least one server is required for a VTP domain.
Client Mode: In client mode, switches synchronise their own VLAN database with servers’ VTP information. Additionally, they forward VTP updates that come in through their trunk ports. Nevertheless, VTP clients are unable to add, modify, or remove VLANs. Client switches usually do not store their VLAN configuration in NVRAM, therefore if the switch is reset or reloaded, the configuration will be erased.
Transparent Mode: When a switch is in transparent mode, it doesn’t take part in the synchronisation of the VTP domain. It keeps up a local VLAN database of its own. On a transparent switch, VLANs can be added, changed, and removed; however, these actions only affect the switch locally and do not affect other switches within the VTP domain. Transparent switches serve as VTP relays, forwarding received VTP ads from their trunk ports.
Also Read About Cisco Basic Switch Configuration Commands step by step guide
VTP Versions
VTP comes in three versions, each with notable variations:
VTP Version 1 (VTPv1)
The initial version, known as VTP Version 1 (VTPv1), supported VLANs with a usual range of 1–1005. On older Cisco switches, this is the default setting.
VTP Version 2 (VTPv2)
Compared to version 1, VTP version 2 offers the following advantages:
- The standard setting on contemporary Cisco switches.
- Transparent VTP switchtransmit VTP packets without verifying the version number and domain name.
- In transparent mode, it supports a wider range of VLANs (1006 to 4094).
- Consistency tests are not carried out when fresh data is received from VTP messages. A received VTP message’s information is accepted if its MD5 digest is accurate.
- It transmits unknown Type-Length-Value (TLVs).
VTP Version 3 (VTPv3)
The most sophisticated and adaptable version, VTP Version 3 (VTPv3), provides additional improvements. Private VLANs, extended-range VLANs (1006-4094), and ads for Multiple-Spanning-Tree (MST) data are all supported. Through the use of primary/secondary servers, VTPv3 offers enhanced authentication and defense against unintentional database overwrites (also known as the “VTP bomb”), giving the VLAN database more control. For more recent networks, it is advised.
VTP Pruning
One function intended to maximise bandwidth usage on trunk links is VTP pruning. Trunk links automatically forward all VLANs’ broadcast, multicast, and unknown unicast data. Switches can electively prune (block) traffic for VLANs with no active ports on the downstream switch that is linked by using VTP pruning. By doing this, unneeded traffic is kept out of trunks, which enhances network performance.
- How it operates: Information about active VLANs is shared between switches. A switch stops forwarding traffic for a specific VLAN across a trunk link if it detects that the VLAN is not present on the other side of the trunk link.
- Eligibility: Generally speaking, VLAN 1 and VLANs 1002–1005 are not eligible for pruning.
- Configuration: On a VTP server, VTP pruning is often activated globally before being distributed to clients.
Advantages of VLAN trunking protocol
- Centralized VLAN management makes it easier to create, remove, and modify VLANs throughout the network.
- Consistency lowers configuration errors by ensuring that every switch in a VTP domain has the same VLAN database.
- Decreased Administration: Network administrators save time and effort by having VLAN changes propagate automatically.
- Dynamic VLAN administration: Offers dynamic VLAN database administration and reporting.
- Plug-and-play: VLAN configurations can be automatically learnt by new switches that are introduced to a VTP domain.
Disadvantages of VLAN trunking protocol
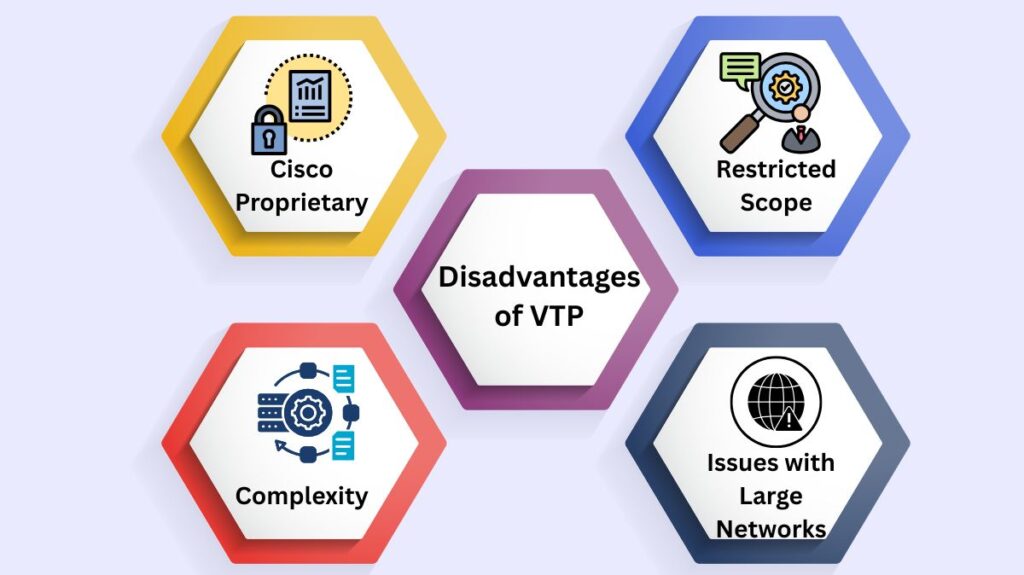
Cisco Proprietary: VTP’s use in multi-vendor situations is restricted because it only functions with Cisco devices.
Security Risks / “VTP Bomb”: The “VTP bomb” is a major worry. A new switch may overwrite the VLAN configurations on all other switches in the VTP domain, causing network failures, if it is unintentionally connected to the network with the correct VTP domain name and password but a higher configuration revision number (even if its VLAN database is empty or incorrect). Better defence against this is provided by VTPv3.
Complexity: Handling version discrepancies or managing several VTP domains can be difficult. The security of older VTP versions (v1, v2) is lower.
Restricted Scope: Only normal-range VLANs (1–1005) are supported by older VTP versions.
Issues with Large Networks: Because there is a greater likelihood of a single error jeopardising the entire network, managing VTP in very large networks can be challenging.
Because of these hazards, a lot of network managers decide to use VTP in transparent mode for more control and security, or disable VTP and manually configure VLANs. VTP is not included in the current CCNA 200-301 test blueprint.
Also Read About MAC Address Tables In Switch For Network Data Forwarding
VLAN trunking protocol configuration
The following conditions must be satisfied in order for VTP to properly transmit VLAN information:
- The VTP version must be the same on every switch in the VTP domain.
- The VTP domain name must be the same for every switch.
- A minimum of one switch needs to be set up as a VTP server.
- All switches in the VTP domain must have the same VTP password if one is being used.
- It is necessary to create trunk links between switches.
Monitoring and Verification
You can monitor VTP operation and status using commands such as show vtp status and show vtp counters. These commands display information like the VTP version, configuration revision, operating mode, domain name, and pruning mode.
