What is Diameter protocol?
The Diameter protocol is an improved network communication protocol that is mostly utilized for IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) designs and Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) services in computer networks, including contemporary mobile settings like 3G, 4G (LTE), and 5G. Having developed from its predecessor, the RADIUS protocol, it is regarded as the next-generation AAA protocol.
Since a diameter is twice the radius, the term “Diameter” is a light-hearted allusion to the RADIUS protocol.
You can also read What is EAP AKA, How it Works, Advantages and Disadvantages
Core Functions (AAA)
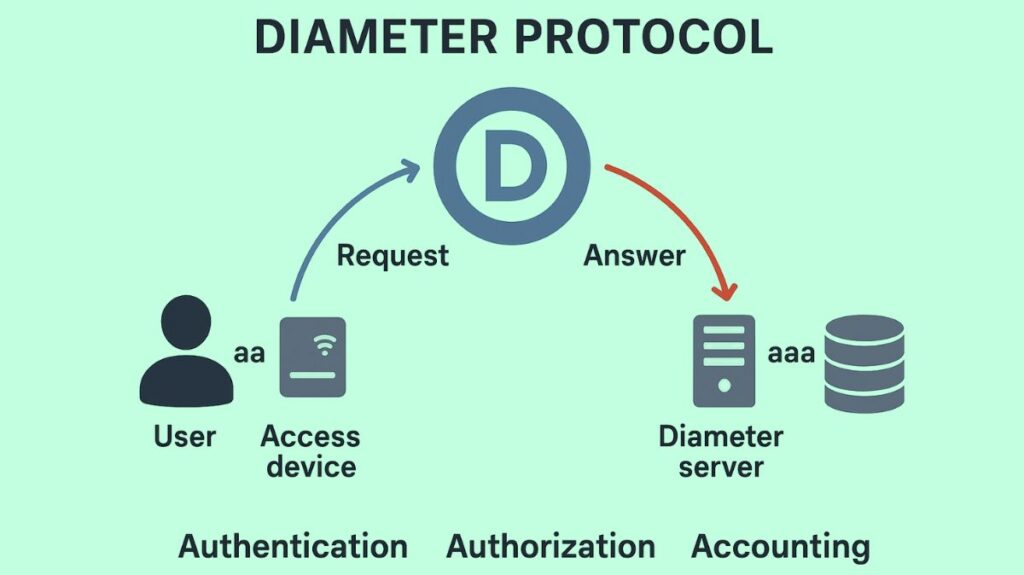
The three primary security and session functions required for network access and service management are managed by Diameter:
- Authentication: Before allowing access, it confirms the user’s identity, for as, by examining a mobile subscriber’s login information.
- Authorization: After successful authentication, authorization establishes the precise services, data access privileges, and quality of service (QoS) that the user is allowed to access.
- Accounting: Keeps track of the resources used (such as data usage and session length) for performance analysis or payment purposes.
Key Features and Improvements over RADIUS
Diameter was developed to overcome the limitations of RADIUS concerning reliability, security, scalability, and flexibility.
| Feature | DIAMETER | RADIUS (Predecessor) |
|---|---|---|
| Transport Protocol | TCP and SCTP (Stream Control Transmission Protocol) (Reliable, connection-oriented) | UDP (Unreliable) |
| Reliability/Failover | High. Defines built-in retransmissions, failover methods, and state machines. | Low. Requires application-layer retransmissions. |
| Security | Mandatory use of IPsec or TLS (Transport Layer Security). | Optional security, often relying only on shared secrets. |
| Architecture | Peer-to-Peer. Any agent can initiate a request. Supports intermediaries (proxies, relays, redirects). | Strictly Client-Server. Server cannot initiate messages. |
| Extensibility | High. Uses flexible Attribute-Value Pairs (AVPs) that are vendor-extensible. | Limited extensibility. |
| Addressing/Attributes | Uses 32-bit address space/boundaries (for AV identifiers). | Uses 8-bit addressing (limited to 256 attribute types). |
| Application | Core network signaling for modern mobile services (4G/5G). | Basic network access (Wi-Fi, VPN, legacy). |
You can also read What is EAP SIM, How it Works, Advantages and Disadvantages
Architecture and Communication
Diameter is structured around a base protocol that works in conjunction with specific Diameter Applications.
Message Structure: Header and AVPs
In Diameter, all data is transferred within Attribute-Value Pairs (AVPs). These are adaptable data structures that contain parameters such as session information, configuration data, and usernames.
A header and a variable number of AVPs make up a Diameter packet. Important routing and state management fields are included in the header:
- Command Code: Identifies the Request/Answer pair; for example, code 271 is used for Accounting-Request/Answer (ACR/ACA).
- Application-ID: Determines the Diameter application the message is associated with (ID 4 is used by the Credit Control Application, for example).
- Hop-by-Hop Identifier: Adjacent Diameter agents (peers) use the Hop-by-Hop Identifier to match requests with their matching responses. When forwarding a request, relaying agents swap out this value.
- End-to-End Identifier: In conjunction with the Origin-Host AVP, the End-to-End Identifier is used to identify duplicate messages throughout the Diameter channel. There are no middle agents that alter it.
- Command Flags: The “R” (Request), “P” (Proxiable), “E” (Error), and “T” (Potentially re-transmitted message) bits are examples of command flags.
Agents and Peers
Peers are interconnected nodes that communicate with one another via diameter. Any Diameter node (client, server, relay, or proxy) that has the ability to send a request to another agent is considered an agent.
Load balancing, processing, aggregation, and the ability to interface with legacy AAA protocols are all provided by intermediate nodes, or agents. Diameter Signalling Controllers (DSCs) are frequently used to centralise routing and protocol mediation, collapsing the mesh into a more straightforward hub-and-spoke topology because the peer-to-peer structure can result in a complicated mesh topology.
Applications and Commands
The minimal specifications for a AAA protocol are outlined in the Diameter Base Protocol. By adding new commands and/or necessary AVPs, Diameter Applications expand upon this fundamental protocol.
Examples of standard Diameter Applications include:
- Diameter Credit-Control Application (DCCA): Mainly used for real-time and prepaid billing.
- Diameter Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) Application: Transports EAP packets from a back-end authentication server to a Network Access Server (NAS).
- Diameter NAS Application (NASREQ): Network access server authentication, authorization, and accounting are handled by the Diameter NAS Application (NASREQ).
Diameter is essential for communication between control-plane components in mobile networks. For example, in 4G (LTE), it interfaces with the Mobility Management Entity (MME), the Policy and Charging Rules Function (PCRF), and the Home Subscriber Server (HSS). To verify a subscriber’s profile and provide initial access, for instance, the HSS employs Diameter instructions. Among the various diameter interfaces specified by 3GPP standards are S6a, Gx, Gy, and Rx.
Analogy: Comparatively speaking, Diameter is a modern, dependable courier service (TCP/SCTP) with required armored transport (TLS/IPsec), detailed, customizable manifest boxes (AVPs), and an intricate logistics hub (Peer-to-Peer architecture) that can route specialized packages (Applications) across international mobile networks. RADIUS would be a simple, unreliable postal service that only operated between your home (client) and the post office (server), relying on slips of paper (8-bit attributes) that could be lost.
You can also read What is EAP FAST, How it Works and Advantages of EAP-FAST
