Extranet and Intranet
What is Extranet VPN?
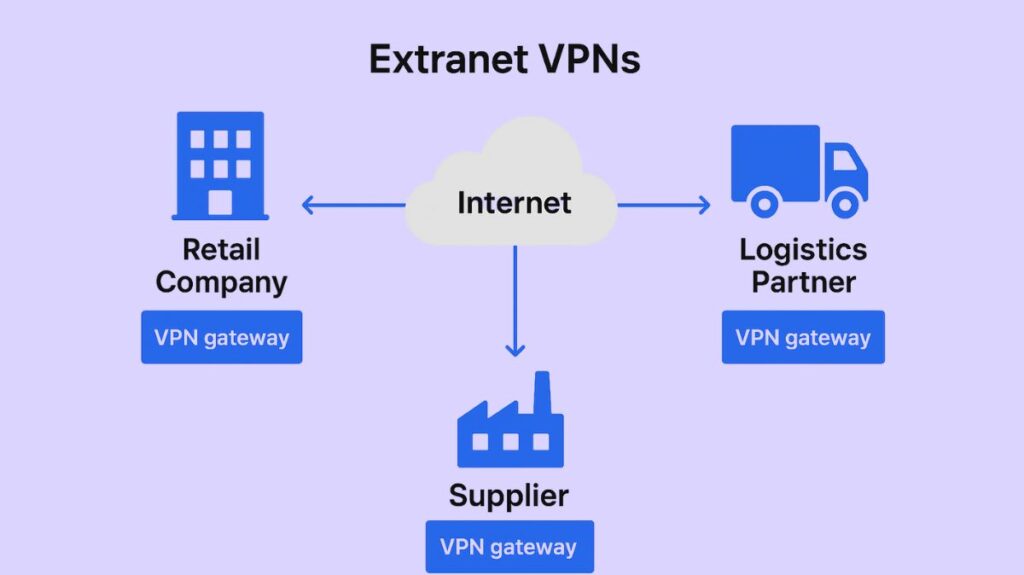
A specialized type of networking called an Extranet Virtual Private Network (VPN) is made to help businesses communicate and work together securely with their approved external partners, including vendors, suppliers, customers, and joint venture partners.
In essence, it functions as a restricted extension of an organization’s private network, or intranet, making it possible for outside parties to connect for business-to-business (B2B) conversations.
You can also read Advantages and Disadvantages of Remote Access VPN & Types
Core Definition and Technology?
- Site-to-Site Connection: An Extranet VPN is mostly classified as a type of Site-to-Site VPN, which links the Local Area Networks (LANs) of two different organizations by creating a network-to-network connection between their VPN gateways (firewalls or routers).
- VPN Foundation: The Extranet creates a private, secure connection over a shared, public infrastructure, usually the World Wide Web, by using VPN technology. An encrypted “tunnel” is formed over the public network using this connection.
- Security Protocols: Protocols such as SSL/TLS (Transport Layer Security) and Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) are used to provide security. As the data moves between sites, these protocols guarantee its validity, integrity, and privacy. For example, IPsec uses protocols like the Authentication Header (AH) or Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) to ensure privacy, integrity, and authentication.
How It Works?
- Every company has a unique VPN gateway and local area network (LAN).
- An encrypted VPN tunnel is established between the organizations by the gateways.
- Only authorized people or systems can communicate with the access control.
Example:
Through an Extranet VPN, a manufacturer and a supplier can exchange inventory data while maintaining the privacy of other internal business information.
Key Characteristics and Security
Extranet VPNs are defined by their strict security and access management requirements:
- Controlled Access: The main purpose is to grant external users extremely limited and regulated access. Instead of having access to the whole internal network of the organization, these outside partners are only permitted to engage with a restricted set of business data and resources.
- Firewall Separation: A firewall is essential for keeping the company’s extremely sensitive internal data (the Intranet) apart from the extranet section that manages business-to-business (B2B) traffic.
- Authentication and Authorization: External users must have strong authentication utilizing techniques like digital certificates, passwords, and user IDs. Access is controlled by authorization policies, which make sure that rights (such as access to particular Web servers or network resources) are based on general roles that the participating businesses have established.
- Security Features: A combination of tunneling, encryption, authentication, and access control methods is used by VPN technology to offer security. Business-to-business communication using the Extranet VPN is intended to be extremely safe, dependable, and controllable.
Purpose and Use Cases
For efficient, automated, and secure digital interactions to replace traditional, human-intensive, paper-based communication (such as faxes, phone calls, or unautomated emails), extranet virtual private networks (VPNs) are essential.
Typical uses consist of:
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): Businesses can monitor production schedules, manage inventory data in real-time, and arrange material delivery by securely connecting with suppliers.
- E-Procurement: E-procurement is the process of automating a business’s network-based purchases of essential goods and services from suppliers, doing away with paper-based transactions.
- Collaborative Projects: Offering a safe, centralized platform for document sharing and collaboration to project teams from many organizations (such as engineering firms or agencies).
- Customer Portals (B2B): B2B customer portals give big company clients safe access to order tracking, account histories, and the ability to submit service tickets.
- Joint Ventures: Safely linking the essential IT systems of two independent businesses that collaborate.
You can also read What is RADIUS Components, Architecture and Applications
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Efficiency: Through automated interactions, it streamlines communication and boosts operational efficiency, frequently producing a win-win scenario for all parties involved.
- Cost Reduction: Lowers expenses in comparison to private leased lines or significant administrative overhead related to travel and paperwork.
- Scalability: Offers an environment that is both adaptable and scalable, making it simple to adjust to evolving business interactions.
- Secure Data Transfer: Enables the safe transmission of substantial volumes of extremely private information over a network.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Security measures are complicated because they necessitate meticulous configuration and monitoring of certain access privileges.
- External Risk: If the networks of external partners connected via the VPN are not sufficiently secured, there are security hazards.
- Hosting/Dependency: The system as a whole depends on internet access, and hosting an extranet may call for high capacity internet connections.
Intranet VPN
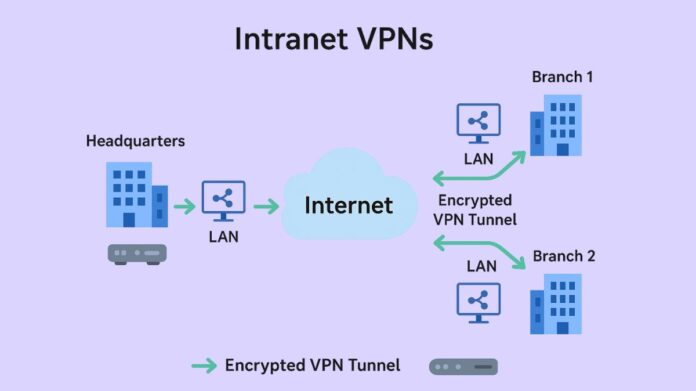
By connecting several locations within the same company, an intranet virtual private network (VPN) establishes a single, private network across public infrastructure. Using VPN technology for encryption and security, it enables workers to work together and share data safely across locations, just like if they were on the same local network.
How it works?
- Site-to-site connection: An intranet VPN connects the whole Local Area Networks (LANs) of various offices to establish a Wide Area Network (WAN), as opposed to just one user connecting to a network.
- Secure communication: It makes the connection as secure as a private network by protecting the data sent between sites via encryption and tunneling.
- Cost-effective: Utilizing the public internet to carry VPN tunnels may be less expensive than utilizing dedicated private lines for connection to wide area networks.
Advantages
- Resource sharing: Regardless of an office’s actual location, it allows for safe access to shared resources and data.
- Cost reduction: It might lower the bandwidth expenses for Wide Area Networks (WAN).
- Increased uptime: By enabling backup lines between several service providers, it can offer network redundancy, boosting uptime.
- Easy expansion: Adding new distant offices or branch sites to the network is simpler.
You can also read What Is Network Based Intrusion Detection System NIDS?
