In this article, we learn about JavaScript Object Notation, JSON’s Role in Automation and APIs, JSON Syntax and Structure, JSON Objects and Arrays, JSON for Configuration Data Example, JSON and Python in Automation, Practical Examples in Cisco Environments, JSON Advantages and JSON Limitations.
JavaScript Object Notation JSON
A fundamental data format that is widely used in network automation and programmability is JavaScript Object Notation (JSON). Along with XML and YAML, it is one of the three widely used data formats. The ability to decipher JSON-encoded data is emphasized in the current CCNA test blueprint.
JSON is a human-readable data format designed for data reading, storage, and transfer applications. Its design seeks to strike a balance between machine parseability and human readability.
You can also read JAVASCRIPT, JQUERY, Node.js
JSON’s Role in Automation and APIs
JSON is a data modelling or serialization language that describes variables, their values, and data structures using text.
- Enabling Application Communication: A standardized internal representation of variables is not a viable option for programs written in different languages. By offering a common text-based format for variables to be represented for storage and communication outside of the program, JSON gets around this. This makes it possible for an API server to return variable names and data structures that the client application can duplicate.
- REST API Integration: JSON is widely used with REST APIs (Representational State Transfer).
- In networking applications, like the Cisco DNA Centre northbound API, it is one of the forms most likely to be delivered in a response from a REST-based server API.
- The controller provides structured data, usually in JSON or XML format, in an HTTP response when an application uses an HTTP GET request to request an object (resource) from a REST API.
- Data Exchange Process: During an API call, the internal variable representation is transformed into a data model (such as a JSON string) by the server’s API code and then transmitted over the network. The JSON-formatted data is subsequently transformed by the REST client into variables appropriate for the native format of the client program (such as a Python dictionary or list). A single line of code can frequently complete this conversion procedure.
- Configuration and Operational Data: Automation scripts retrieve operational data (CPU, memory, interface status, counters, logs) and configure devices (interfaces, VLANs, etc.) using JSON payloads.
- Controller Automation: To push templates, manage topologies, and retrieve telemetry, SDN controllers such as Cisco DNA Centre and Cisco vManage heavily rely on JSON. JSON is also used by cloud platforms to manage resources like security groups and VPCs.
You can also read Future of Network Automation and Types of Network Automation
JSON Syntax and Structure
JSON uses straightforward, comprehensible conventions that are taken from JavaScript grammar to organize data. JSON uses key:value pairs to define data.
Key:Value Pairs Rules
The key and value are separated by a colon (:).
- Key: Must be text enclosed in double quotes (e.g.,
"name"). The key serves as the name referencing the value. - Value: The value can be one of several types:
- Text: Must be listed in double quotes.
- Numeric: Listed without quotes.
- Boolean: Must be lowercase.
- Array or Object (complex data structures).
- Multiple Pairs: When listing multiple key:value pairs, they must be separated by a comma, except for the last pair. Trailing commas must not be used.
JSON Objects and Arrays
JSON uses objects and arrays to represent complex data structures.
JSON Object {}: Represents a series of key:value pairs enclosed in curly brackets ({}). A JSON file or API response typically exists first as a single JSON object. JSON objects are converted to Python dictionaries.
{
"device_name": "RTR-NYC-01",
"device_type": "router"
}
JSON Array []: Represents a series of values (not key:value pairs) enclosed in square brackets ([]). If a key has a square bracket as its value, it indicates that the key corresponds to multiple values or a collection. JSON arrays are converted to Python lists.
"vlans": [
{ "id": 10, "name": "DATA_VLAN" },
{ "id": 20, "name": "VOICE_VLAN" }
]
Nesting: JSON supports nesting, where values can contain objects and arrays in various combinations.
Formatting for Readability
JSON accommodates formatting preferences for different use cases:
- Minified (Raw): JSON usually doesn’t utilize whitespace when it’s transferred over a network or stored in a file. This computer-optimized form is sometimes known as raw or minified.
- Beautified (Pretty): Tools enable switching to a “pretty” format for human consumption, which takes advantage of alignment and spacing to make the text simpler to read.
You can also read What is MP BGP Multiprotocol BGP? Components and Benefits
JSON for Configuration Data Example
The JSON payload must adhere exactly to the YANG model’s structure when setting a network device using a model-driven method (such as RESTCONF).
Here is a simplified example of configuring an interface, using a structure often dictated by an IETF or vendor YANG model:
{
"ietf-interfaces:interface": [
{
"name": "GigabitEthernet1/0/1",
"enabled": true,
"description": "UPLINK_TO_CORE",
"type": "iana-if-type:ethernetCsmacd",
"ietf-if-types:ethernet": {
"auto-negotiation": true,
"speed": 1000
},
"ietf-ip:ipv4": {
"address": [
{
"ip": "192.168.1.1",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0"
}
]
}
}
]
}
ietf-interfaces:interface: This is an array (list) because a device can have many interfaces.name: A simple key-value pair, used as an identifier.ietf-ip:ipv4: A nested object (dictionary) containing parameters specific to IPv4 configuration.
JSON and Python in Automation
JSON’s greatest advantage in automation is its seamless integration with Python, the language of choice for many network engineers. Python’s built-in json module is used for serialization and deserialization.
| Python json Function | Operation | Description |
json.dumps() | Serialization | Converts a Python object (like a dictionary) into a JSON formatted string. |
json.loads() | Deserialization | Parses a JSON formatted string (e.g., from an API response) into a Python object. |
json.dump() | Serialization to File | Writes a Python object directly to a JSON file. |
json.load() | Deserialization from File | Reads a JSON file and converts its content into a Python object. |
This process allows an automation script to:
- Read input data from a
.jsonfile (json.load()). - Build complex configuration data as a Python dictionary.
- Serialize that dictionary to a JSON string (
json.dumps()). - Send the JSON string as the payload in an HTTP POST/PUT request to a network device API.
- Receive a JSON response, and deserialize it back into a Python object (
json.loads()) for processing.
You can also read What is Metro Ethernet Network? how does metro ethernet work
Practical Examples in Cisco Environments
JSON is integral to operational tasks and configuration management in Cisco architectures:
- Cisco DNA Center: The centralized controller’s REST API returns network data to automation programs primarily in JSON format. This data is formalized and defined through data models, allowing automation scripts to retrieve structured facts easily via Northbound APIs, rather than having to parse unstructured text output from
showcommands. - Device Output Conversion: Cisco Nexus devices can natively convert
showcommand output to JSON using a pipe command, such as| json-pretty native. - Configuration Management Tools: While YAML is commonly used by Ansible for defining logic (playbooks) and variables, JSON is supported and understood within this automation ecosystem.
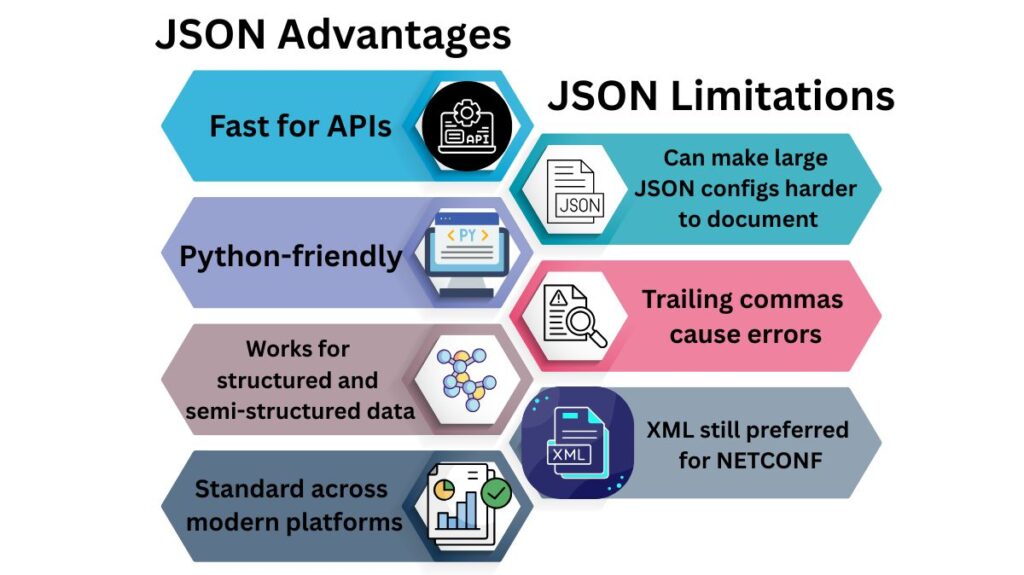
JSON Advantages
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Lightweight | Fast for APIs |
| Easy to parse | Python-friendly |
| Flexible | Works for structured and semi-structured data |
| Multivendor support | Standard across modern platforms |
JSON Limitations
| Limitation | Impact |
|---|---|
| No comments | Can make large JSON configs harder to document |
| Strict syntax | Trailing commas cause errors |
| Less hierarchical than XML | XML still preferred for NETCONF |
You can also read What is Message Switching & advantages of message switching
