NCP Network Control Protocol
One of the core protocols of the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) suite is the Network Control Protocol (NCP). Two computers that are directly connected can exchange multiprotocol data using the PPP data connection layer protocol.
The Link Control Protocol (LCP), Authentication Protocol (AP), and Network Control Protocols (NCPs) are the three primary parts of PPP. The last required set of protocols that function to configure the network layer protocols is called NCPs.
You can also read What is HDLC Protocol High Level Data Link Control Protocol
Role and Function of NCPs
Data transport for many network protocols over a single link is made possible by NCPs. Enabling and controlling the particular Layer 3 (Network Layer) protocols that will operate over the created PPP connection is their main responsibility.
Key roles include:
- Negotiation of Parameters: Network layer-specific parameters and facilities are negotiated using NCPs. Network-layer addresses are frequently requested and assigned during this procedure.
- Configuration and Establishment: They set up and configure the network layer protocols required for PPP connection transit. For example, IP settings are negotiated by the Internet Protocol Control Protocol (IPCP).
- Multiprotocol Support: PPP can provide multiprotocol transport since NCPs allow several Network layer protocols (such as IP, IPX, and AppleTalk) to be carried concurrently over the same PPP link.
- Activation and Control: To get the network layer ready for data flow, NCPs configure it. Network protocol modules on both ends of the PPP link must be configured, enabled, and disabled by them.
- Termination: When LCP terminates the PPP link, NCPs offer a way to cleanly end the network layer protocol.
You can also read What is Packet Switching WAN Technology and Mechanisms
NCP Operation within PPP
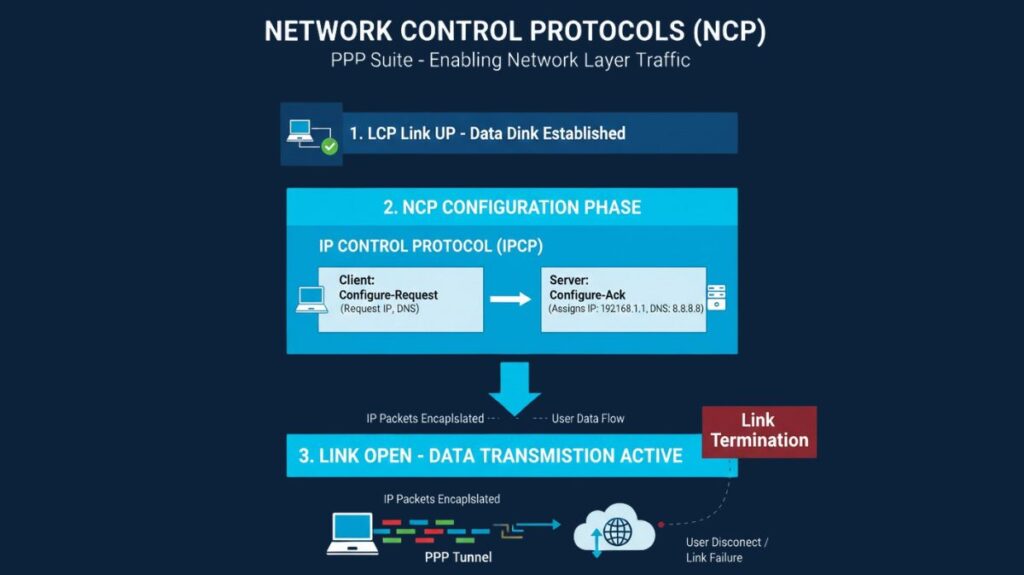
NCP operations follow a specific sequence after the physical link is established:
LCP Phase: The physical link itself must be established, configured, and acknowledged via the Link Control Protocol (LCP).
Authentication Phase: PAP/CHAP and other optional authentication protocols may be used.
NCP Phase: The NCP assumes responsibility for configuring the network layer after LCP is finished. PPP endpoints negotiate protocol-specific settings by exchanging NCP packets (e.g., using Configure-Request and Configure-Ack).
Data Flow: The relevant network protocol is activated and user data transfer starts when the NCP achieves the Opened state.
Examples of Specific Network Control Protocols
A key architectural feature of NCPs is that a separate NCP exists for every higher-layer protocol supported by PPP.
Examples mentioned in the sources include:
| NCP Protocol | Corresponding Network Layer Protocol | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Internet Protocol Control Protocol (IPCP) | Internet Protocol (IPv4) | Establishes and configures IPv4 over the link, including configuring IP addresses and DNS server addresses. |
| IPv6 Control Protocol (IPV6CP) | Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) | Configures the IPv6 addresses and enables/disables IP protocol modules over PPP. |
| Internetwork Packet Exchange Control Protocol (IPXCP) | Internet Packet Exchange (IPX) | Configures, enables, and disables IPX modules, negotiating IPX address and routing parameters. |
| OSI Network Layer Control Protocol (OSINLCP) | OSI Network Layer (CLNP) | Configures, enables, and disables the OSI protocol modules and parameters. |
| NetBIOS Frames Control Protocol (NBFCP) | NetBIOS Frames (NBF) | Configures, enables, and disables the non-routable NBF protocol modules. |
| DECnet Phase IV Control Protocol (DNCP) | DECnet Phase IV Routing protocol | Responsible for establishing and configuring DECnet Phase IV modules over the PPP link. |
To understand the relationship between LCP and NCP, you can think of it this way: LCP is like setting up the dedicated physical pipe between two points, ensuring it’s sealed and ready to carry traffic. The NCPs, in contrast, act as the customs agents and configuration specialists inside the pipe, defining exactly what kind of network traffic (IP, IPv6, IPX) is allowed to flow and what addresses they must use.
You can also read What is a Leased Line Benefits and Types of Leased Lines
