Basic Switch Configuration Commands
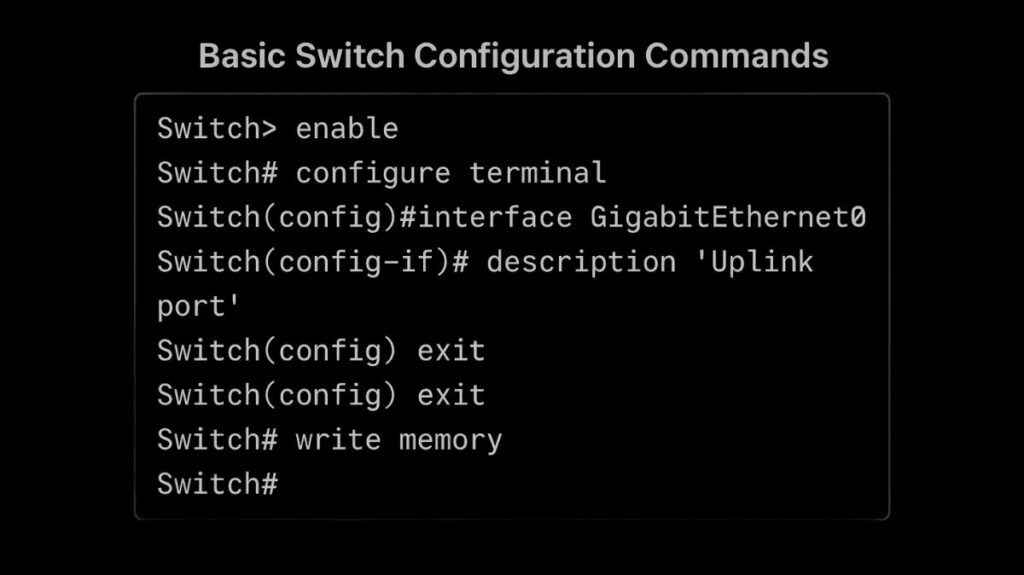
Cisco switches are configured using the Command-Line Interface (CLI), which provides a text-based interface where commands are typed and responses are displayed.
Configuration Modes and Navigation
- In order to start configuring a switch, you usually use the
configure terminalcommand from privileged EXEC mode to enter global configuration mode. You can make adjustments in this mode that impact the router or switch as a whole. - There are numerous subconfiguration modes available in CISCO IOS, starting with global configuration mode. Context-specific submodes group instructions associated with specific components or features, like VLANs or interfaces.
- The current configuration mode is reflected in the command prompt, which changes to
(config)for global,(config-if)for interface,(config-line)for line, and(config-vlan)for VLAN. - The exit command can be used to leave a subconfiguration mode and go to the next higher mode, or you can use the
endcommand orCtrl+Zto go straight back to enable mode from any configuration submode.
You can also read CISCO Switch Configuration: A Safe and Effective Setup Guide
Basic Switch Management Commands
Setting Hostname: The device’s name is set via the hostname name global command, which also makes an appearance on the command prompt.
Password Configuration:
- Enable Password:
enable password pass-value(stored in clear text).enable secret pass-value(stored as an encrypted hash, supersedesenable password).
- Console and VTY Passwords:
- Enter line configuration mode using
line console 0for the console orline vty 0 15for virtual terminal lines (Telnet/SSH). - Use the
password pass-valuesubcommand to set the password. - The
logincommand tells IOS to prompt for a password.
- Enter line configuration mode using
- For local username/password authentication, use
login local.service password-encryptionis a global command that encrypts all clear-text passwords in the running configuration.
- SSH and Telnet Access:
transport input {telnet | ssh | all | none}in vty line configuration mode defines allowed access methods.- SSH requires generating encryption keys using the
crypto key generate rsaglobal command. You also set theip domain-name fqdnglobal command for SSH.
You can also read Understanding Switching Logic: The Brain Of A Network Switch
Interface Configuration Commands
Entering Interface Mode:
- To configure a single interface, use the
interface type port-numberglobal command. - To configure multiple interfaces simultaneously, use the
interface range type port-number - end-port-numberglobal command. Subsequent subcommands apply to all interfaces in that range.
Administrative Interface Control:
- The
shutdowninterface subcommand administratively disables an interface. - The
no shutdowninterface subcommand enables an interface.
Speed and Duplex Settings:
speed {10 | 100 | 1000 | auto}manually sets the speed or enables autonegotiation.duplex {auto | full | half}manually sets the duplex mode or enables autonegotiation.
Description: The description text interface subcommand allows you to add a text description to an interface for documentation purposes.
VLAN and Trunking Configuration
Creating VLANs: The vlan vlan-id global command creates a VLAN and enters VLAN configuration mode.
Assigning Access Ports:
switchport mode accessconfigures an interface to be a static access port.switchport access vlan vlan-idassigns a specific VLAN to an access port.switchport voice vlan vlan-iddefines a voice VLAN for ports connected to IP phones.
Trunk Port Configuration:
switchport mode trunkconfigures an interface as a static trunk port.switchport trunk encapsulation dot1qspecifies 802.1Q as the trunking encapsulation method.switchport mode dynamic {auto | desirable}configures dynamic trunk negotiation.switchport nonegotiatedisables Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) negotiation.switchport trunk allowed vlan vlan-listdefines which VLANs are permitted to traverse the trunk.switchport trunk native vlan vlan-iddefines the native VLAN for an 802.1Q trunk port.
VLAN Administrative Control:
[no] shutdown vlan vlan-id(global configuration mode) or[no] shutdown(VLAN configuration mode) can be used to enable or disable a VLAN.
You can also read What is Frame Forwarding and Frame Forwarding Methods
Port Security Configuration
switchport port-securityenables port security on an interface.switchport port-security maximum numberoverrides the default maximum number of allowed MAC addresses (default is 1).switchport port-security mac-address stickyconfigures the switch to learn MAC addresses dynamically and save them to the running configuration as secure MAC addresses.switchport port-security mac-address mac-addressstatically adds a specific MAC address as an allowed MAC address on the interface.switchport port-security violation {protect | restrict | shutdown}overrides the default action (shutdown) when a security violation occurs. A port shut down due to a security violation will show aserrdisabledand requiresshutdownthenno shutdownto recover.
EtherChannel Configuration
- The
channel-group number mode {auto | desirable | active | passive | on}interface subcommand enables EtherChannel on an interface. activemode initiates LACP negotiation, whilepassivemode responds to LACP packets without initiating negotiation.onmode unconditionally forces the interfaces to form an EtherChannel without negotiation.- Configuring EtherChannel automatically creates a logical
interface port-channel channel-numberfor overall management.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Configuration
spanning-tree mode {pvst | rapid-pvst | mst}(global command) sets the STP mode for the switch.spanning-tree portfast(interface subcommand) configures a port to immediately transition to forwarding mode, bypassing normal STP states.spanning-tree bpduguard enable(interface subcommand) enables BPDU Guard to protect access ports from receiving BPDUs.- Alternatively, global commands
spanning-tree portfast defaultandspanning-tree bpduguard defaultenable PortFast and BPDU Guard on all access ports.
Miscellaneous Commands
ip address ip-address maskconfigures an IP address on a Layer 3 interface, such as a VLAN interface.ip default-gateway ip-address(global command) sets the default gateway for the switch.ip name-server ip-address1 ip-address2(global command) configures DNS servers for name resolution on the switch.[no] lldp run(global command) and[no] lldp receive(interface subcommand) control LLDP operation on the device and interfaces.
Verification Commands
- To confirm and debug network performance, show commands are crucial.
- Examples include
show running-config(current configuration),show interfaces [type number] status(interface status, speed, duplex), andshow vlan brief(VLAN status).
Key Configuration Commands
| Command | Description | Example |
hostname [name] | Sets the switch’s hostname. | hostname SW-HQ |
interface [interface-id] | Enters interface configuration mode for a specific port. | interface GigabitEthernet 0/1 |
description [text] | Adds a description to an interface. | description PC-User-1 |
switchport mode access | Configures the port as an access port for a single VLAN. | switchport mode access |
switchport access vlan [vlan-id] | Assigns the access port to a specific VLAN. | switchport access vlan 10 |
switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q | Sets the trunking protocol to 802.1Q. | switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q |
switchport mode trunk | Configures the port as a trunk port, carrying multiple VLANs. | switchport mode trunk |
ip address [ip-address] [subnet-mask] | Assigns an IP address to a VLAN interface (SVI). | ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 |
no shutdown | Activates an interface. | no shutdown |
exit | Exits the current configuration mode. | exit |
end | Returns to privileged EXEC mode from any configuration mode. | end |
copy running-config startup-config | Saves the active configuration to NVRAM, so it persists after a reboot. | copy running-config startup-config |
show running-config | Displays the current configuration in RAM. | show running-config |
show vlan brief | Displays a summary of all configured VLANs. | show vlan brief |
show mac address-table | Displays the MAC address table. | show mac address-table |
You can also read Broadcast and Collision Domains, Advantages & Disadvantages
